Duodenitis - Symptoms, Treatment and Home Remedies
contents
- anatomy
- Tasks of the duodenum
- Inflammation - acute or chronic
- causes
- to form
- symptoms
- Diagnosis, examination possibilities
- Helicobacter pylori
- Therapy Helicobacter
- Therapy for duodenitis
- Help from naturopathy
- complications
anatomy
The stomach is followed by the upper part of the small intestine. This is the duodenum. It is C-shaped and encloses the head of the pancreas. Their excretory duct and also the bile duct terminate together in the so-called papilla vateri in the duodenum.
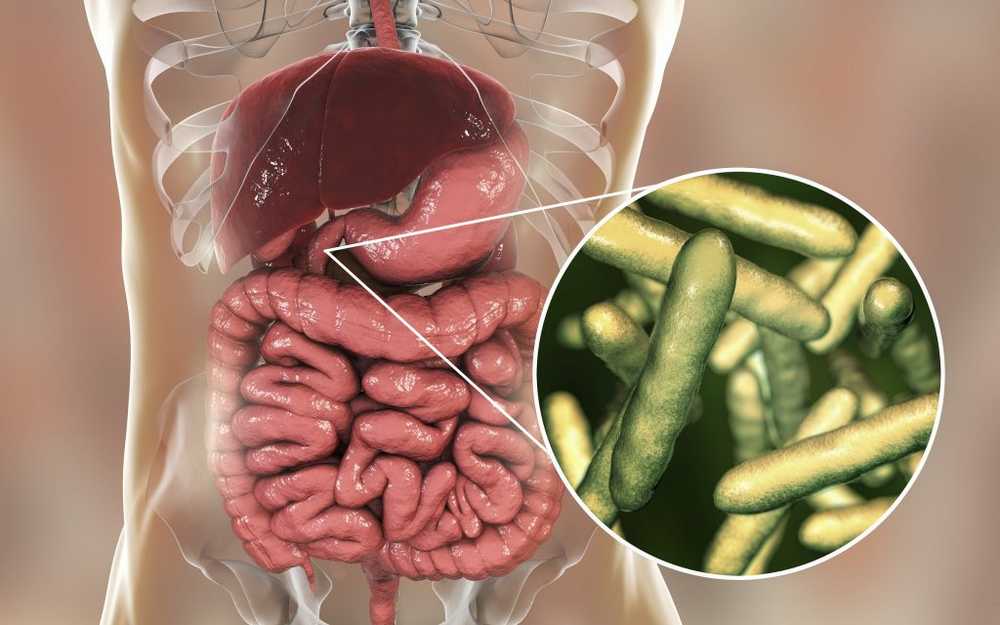
 A duodenitis is often due to infections with the bacterium Helicobacter pylori, but can also be caused by numerous other factors. (Image: Kateryna_Kon / fotolia.com)
A duodenitis is often due to infections with the bacterium Helicobacter pylori, but can also be caused by numerous other factors. (Image: Kateryna_Kon / fotolia.com) Tasks of the duodenum
Digestion begins in the mouth and then continues in the stomach. The next stage is then the small intestine and first of all the duodenum. Here, the gallbladder releases its secretions and the pancreas its enzymes. From the pancreas an alkaline liquid is added to neutralize the chyme, as it is quite acidic due to the stomach acid. The digestion continues its course.
Inflammation - acute or chronic
A duodenitis can be both acute and chronic. Often she is not noticed by those affected. The inflammation occurs primarily or secondarily. Primary means that, for example, a pathogen (often Helicobacter pylori) is responsible for this. Secondary states that duodenal inflammation is a concomitant disease to other already existing diseases in the digestive tract.
causes
Causes of developing duodenitis include infections of the gastrointestinal tract by viruses, bacteria and other agents. The main culprit here is, as already mentioned, the bacterium Helicobacter pylori. Other triggers of a duodenitis are drugs - especially the longer use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs such as acetylsalicylic acid, diclofenac, naproxen and ibuprofen. For secondary duodenitis, causes such as a Duodenalulcus (duodenal ulcer), bile duct and stomach diseases into consideration.
to form
In medicine, duodenitis is divided into various forms. There is, for example, an erosive duodenitis, which means that the inflammation is associated with a superficial tissue loss. In the fibrinous form so-called fibrin deposits form. These are caused by the adhesion of platelets (platelets) during wound healing. The edematous form is associated with swollen mucous membrane, the phlegmonous with pus formation, in the polypoid form develop polyps and the stenosing form shows constricted areas.
symptoms
Often, a duodenitis does not make itself felt by those affected. Here a random diagnosis brings the whole thing to light. However, typical symptoms of duodenitis may be
- stinging or oppressive pain under the right costal arch,
- anorexia,
- Nausea and vomiting,
- general malaise,
- burping,
- bloating,
- Diarrhea and constipation (both may be alternating).
For complaints such as blood in the stool, vomiting blood and / or severe pain, consult a doctor as soon as possible.
 Pain in the area of the lower costal arch is a typical sign of duodenitis. (Image: Adiano / fotolia.com)
Pain in the area of the lower costal arch is a typical sign of duodenitis. (Image: Adiano / fotolia.com) Diagnosis, examination possibilities
If a suspicion of a duodenitis is suspected, the doctor first of all makes an overall picture of the patient through a detailed medical history. Pre-existing conditions, medication, nutritional habits, type of pain and other complaints are queried. This is followed by a palpation of the abdomen, a sonography, possibly X-ray examinations and / or a duodenal endoscopy with biopsy.
At endoscopy, a thin tube with a camera passes over the esophagus and stomach into the duodenum. So shots are taken and at the same time, with the help of a small instrument, which is also attached to the tube, if necessary (for example, if polyps are present) some tissue can be removed. Patients may stay awake during the exam. Mostly, however, this is done under a short anesthetic.
Helicobacter pylori
Helicobacter pylori is a bacterium that colonizes the gastrointestinal tract and can cause a variety of diseases. For example, a chronic gastritis (gastritis) or a duodenitis. How this bacteria gets into the body, is still not fully understood. The discussion is concerned with fecal contaminated food and contaminated water. So far, it remains uncertain whether a mouth-to-mouth infection is possible.
Who smokes, often drinks alcohol, has an immunodeficiency and / or is under massive stress, can more easily infected with Helicobacter pylori. Also, medications such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (see Causes) can increase the risk that colonizes this bacterium. An infection is detected, for example, in the context of a gastroscopy, duodenal endoscopy, by blood or stool examinations and with the help of a so-called breath test.
Therapy Helicobacter
The usual therapy for Helicobacter infection is as follows: A combination of antibiotics and gastric protection is administered. This therapy is often referred to as eradication therapy, which means "eradicate, completely eliminate" means. This will take up to fourteen days. It is then re-examined to see if the bacterium has really disappeared.
 In case of duodenitis, it is urgently necessary to dispense with indigestible, high-fat and too sweet food. (Image: happy_lark / fotolia.com)
In case of duodenitis, it is urgently necessary to dispense with indigestible, high-fat and too sweet food. (Image: happy_lark / fotolia.com) Therapy for duodenitis
If drugs are responsible for the development of duodenitis, they should of course be discontinued or replaced by other drugs. If a Helicobacter pylori infection is the cause, the bacterium is fought (see Therapy Helicobacter). In some cases, even a stomach acid blocker is sufficient, which is prescribed for a short time. The diet is definitely to rethink. Hard to digest, rich in fat and too sweet food is to be avoided.
The diet should be basic in any case. Spicy spices, bloating and raw food are not on the menu. Home remedies such as gruel or linseed decoction have a healing component. For the flaxseed soup, two to three tablespoons of ground flaxseed are soaked overnight in half a liter of water, boiled briefly the next day, and then strained. The slimy liquid is drunk throughout the day.
Great meals are definitely to be avoided. Chew every bite extensively and take your time eating. Cold drinks are prohibited. Better is lukewarm water or herbal tea.
Since stress is considered to be a cause of duodenitis, relaxation techniques such as yoga, meditation or autogenic training are recommended.
 Bitter herbs such as dandelion, wormwood, galangal, cinnamon and ginger may aid the treatment of duodenitis. (Image: creativefamily / fotolia.com)
Bitter herbs such as dandelion, wormwood, galangal, cinnamon and ginger may aid the treatment of duodenitis. (Image: creativefamily / fotolia.com) Help from naturopathy
Even if the duodenitis is treated by conventional medicine, naturopathy can also serve well. Plants such as chamomile, licorice, myrrh or plantain, as tea or as tincture, are recommended here. What has a positive effect on the mucous membrane is St. John's wort oil. However, not every oil is suitable here. This should definitely be intended for oral administration. St. John's wort oil clothes the mucous membrane, heals and protects.
Also bitter herbs such as wormwood, galangal, cinnamon, ginger, dandelion, carnation, yarrow, calamus can help. They are basic and thus counteract hyperacidity. In addition, the intake of a base powder helps.
Of the Schuessler salts, No. 3 Ferrum phosphoricum, No. 4 potassium chloratum, No. 5 potassium phosphoricum, No. 9 sodium phosphoricum, No. 10 sodium sulfuricum and No. 20 potassium aluminum sulfuricum are recommended.
Acupuncture and foot reflexology are also forms of therapy that can provide relief in duodenitis. In addition, potato juice is often prescribed for gastritis and gastric ulcer. This is also recommended here. You can buy the potato juice in a health food store. The intake of grapefruit seed extract, aloe vera, manuka honey and cistus tea has an antibacterial effect.
 On the basis of a Zwöffingerdarmentzündung ulcers can form and also threatens a spread of the inflammation on other organs. (Image: Henrie / fotolia.com)
On the basis of a Zwöffingerdarmentzündung ulcers can form and also threatens a spread of the inflammation on other organs. (Image: Henrie / fotolia.com) complications
Untreated duodenitis can lead to duodenal ulcer (duodenal ulcer). Furthermore, it is possible to spread the inflammation to other organs. In the case of the above-mentioned complaints, a doctor should definitely be consulted and the disease cured and treated. (Sw)
Specialist supervision: Barbara Schindewolf-Lensch (doctor)


